简单记录一下学习completableFuture的过程,记录的逻辑可能不太通顺,可以阅读末尾参考文章
作用
CompletableFuture继承了future,future可以获取线程执行的结果,线程执行后返回一个future,通过future获取线程执行结果。compaltedfuture可以获取异步线程的执行结果。可以进行并行操作
- Future用于表示异步计算的结果,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式获取结果,而且不支持设置回调方法,Java 8之前若要设置回调一般会使用guava的ListenableFuture,回调的引入又会导致臭名昭著的回调地狱(下面的例子会通过ListenableFuture的使用来具体进行展示)。
- CompletableFuture对Future进行了扩展,可以通过设置回调的方式处理计算结果,同时也支持组合操作,支持进一步的编排,同时一定程度解决了回调地狱的问题。
创建
cf的参数是一个函数,因此可以实现函数式编程,使用lamba表达式,比较简便。
获取cf实例,可以通过new一个,也可以通过静态工厂方法。
-
通过new关键字
CompletableFuture<RpcResponse<Object>> resultFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();complete可以为cf传入一个结果值。
resultFuture.complete(rpcResponse);根据supplier创建CompletableFuture任务
//使用内置线程ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)//指定自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)根据runnable创建CompletableFuture任务
//使用内置线程ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)//指定自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)- 使用示例
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<Void> rFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("hello siting"), executor);//supplyAsync的使用CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.print("hello ");return "siting";}, executor);//阻塞等待,runAsync 的future 无返回值,输出nullSystem.out.println(rFuture.join());//阻塞等待String name = future.join();System.out.println(name);5 collapsed linesexecutor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭--------输出结果--------hello sitingnullhello siting常量值作为CompletableFuture返回
//有时候是需要构建一个常量的CompletableFuturepublic static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) //带有executor参数的表示,可以自定义线程池作为参数,执行异步任务,不自定义则使用默认的线程池,推荐自定义。
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)run标识没有返回值,参数是runnable,supply标识有返回值。
获取结果
public T get()public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)public T join() //join和get一样会阻塞后面线程。不使用上面方法去获取结果,线程任务依然执行。(单纯新建一个completableFuture,不去get获取结果,这个任务依然在建立的时候回去运行,类似于thread的start()方法)
getNow有点特殊,如果结果已经计算完则返回结果或者抛出异常,否则返回给定的valueIfAbsent值。
join返回计算的结果或者抛出一个unchecked异常(CompletionException),它和get对抛出的异常的处理有些细微的区别,你可以运行下面的代码进行比较:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { int i = 1/0; return 100;});//future.join();future.get()计算结果完成时的处理
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>,可以处理两个参数,一个是结果,一个是异常。
方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
注意这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常。
- whenComplete与handle的区别在于,它不参与返回结果的处理,把它当成监听器即可
- 即使异常被处理,在CompletableFuture外层,异常也会再次复现
- 使用whenCompleteAsync时,返回结果则需要考虑多线程操作问题,毕竟会出现两个线程同时操作一个结果
使用示例
CompletableFuture<AtomicBoolean> first = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("main error!"); } return "hello world"; }) .thenApply(data -> new AtomicBoolean(false)) .whenCompleteAsync((data,e) -> { //异常捕捉处理, 但是异常还是会在外层复现 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); });first.join();--------输出结果--------java.lang.RuntimeException: main error!Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: main error! ... 5 more-
如果之前的处理环节有异常问题,则会触发exceptionally的调用相当于 try…catch
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("main error!");}return "hello world";}).thenApply(data -> 1).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace(); // 异常捕捉处理,前面两个处理环节的日常都能捕获return 0;});
completeExceptionally
-
如果你想让
CompletableFuture的结果就是异常的话,可以使用completeExceptionally()方法为其赋值。 -
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();// ...completableFuture.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("Calculation failed!"));// ...completableFuture.get(); // ExecutionException
handle也返回CompletableFuture对象,但是对象的值和原来的CompletableFuture计算的值不同。当原先的CompletableFuture的值计算完成或者抛出异常的时候,会触发这个CompletableFuture对象的计算,结果由BiFunction参数计算而得。因此这组方法兼有whenComplete和转换的两个功能。
handle-任务完成或者异常时运行fn,返回值为fn的返回,相比exceptionally而言,即可处理上一环节的异常也可以处理其正常返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("main error!"); } return "hello world"; }) .thenApply(data -> 1) .handleAsync((data,e) -> { e.printStackTrace(); // 异常捕捉处理 第一个出现异常第二个不执行,直接进入hadle return data; });System.out.println(first.join());--------输出结果--------java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: main error! ... 5 morenullpublic <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)串行执行/一元依赖
-
thenApply()-
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)//非异步public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)//异步,默认线程池public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)//异步,自定义线程池,推荐。
可以理解为转化,因为有返回值,把上一个cf转变成另一个。
-
-
thenAccept()-
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)//非异步public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action)//异步,默认线程池public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)//异步,自定义线程池,推荐。
可以理解为消费,没有返回值,只利用上一个的结果作为参数进行处理。
-
-
thenRun()-
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action)public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action)public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action, Executor executor)
-
thenApply() 方法接受一个 Function 实例,用它来处理结果。有返回值
thenAccept() 方法的参数是 Consumer<? super T> 。接收cf的结果,但是没有返回值
thenRun() 的方法是的参数是 Runnable 。不接受结果,相当于上一个执行后,自己做自己的事情,有时间关系,没有数据传输关系。
因此,你可以根据方法的参数的类型来加速你的记忆。
Runnable类型的参数会忽略计算的结果,Consumer是纯消费计算结果,BiConsumer会组合另外一个CompletionStage纯消费,Function会对计算结果做转换,BiFunction会组合另外一个CompletionStage的计算结果做转换。CompletionStage表示cf的一个阶段,参数是CompletionStage,标识一个cf作为参数。
并行执行---组合/二元依赖,thencompose算一元依赖
**thenCompose() **
-
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor)
这一组方法接受一个Function作为参数,这个Function的输入是当前的CompletableFuture的计算值,返回结果将是一个新的CompletableFuture,这个新的CompletableFuture会组合原来的CompletableFuture和函数返回的CompletableFuture。
接受上一个任务的返回值作为参数,存在先后顺序有返回值。
- 类似thenApply(区别是thenCompose的返回值是CompletionStage,thenApply则是返回 U),提供该方法为了和其他CompletableFuture任务更好地配套组合使用。Function<T,R>,T是输入,R是返回。
因此它的功能类似:
A +--> B +---> C//第一个异步任务,常量任务CompletableFuture<String> f = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("OK");//第二个异步任务ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello world", executor).thenComposeAsync(data -> {System.out.println(data); return f; //使用第一个任务作为返回,也可以自定义一个completableFuture}, executor);System.out.println(future.join());executor.shutdown();--------输出结果--------hello worldOK //返回的是第一任务,得到的值就是第一个的ok9 collapsed linesCompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 100;});CompletableFuture<String> f = future.thenCompose( i -> {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return (i * 10) + ""; //compose返回值是CompletionStage。retuen});});System.out.println(f.get()); //1000
thenCombine()
-
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor)
两个CompletionStage是并行执行的,它们之间并没有先后依赖顺序,
other并不会等待先前的CompletableFuture执行完毕后再执行。thenCombine是,两个CompletableFuture并行执行完,然后执行fn,依赖上两个任务的结果,有返回值
那
thenCompose()和thenCombine()有什么区别呢?thenCompose()可以两个CompletableFuture对象,并将前一个任务的返回结果作为下一个任务的参数,它们之间存在着先后顺序。thenCombine()会在两个任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果合并。两个任务是并行执行的,它们之间并没有先后依赖顺序。
runAfterBoth
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action)public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action)public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor)两个CompletableFuture并行执行完,然后执行action,不依赖上两个任务的结果,无返回值
thenAcceptBoth
//调用方任务和other并行完成后执行action,action再依赖消费两个任务的结果,无返回值public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action)//两个任务异步完成,fn再依赖消费两个任务的结果,无返回值,使用默认线程池public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action)//两个任务异步完成,fn(用指定线程池执行)再依赖消费两个任务的结果,无返回值public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor)两个CompletableFuture并行执行完,然后执行action,依赖上两个任务的结果,无返回值
thenAcceptBoth和runAfterBoth是当两个CompletableFuture都计算完成,either是当任意一个CompletableFuture计算完成的时候就会执行。Either
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T,U> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T,U> fn)public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T,U> fn, Executor executor)acceptEither方法是当任意一个CompletionStage完成的时候,action这个消费者就会被执行。这个方法返回CompletableFuture
applyToEither方法是当任意一个CompletionStage完成的时候,fn会被执行,它的返回值会当作新的CompletableFuture<U>的计算结果。
多元依赖:依赖多个CF
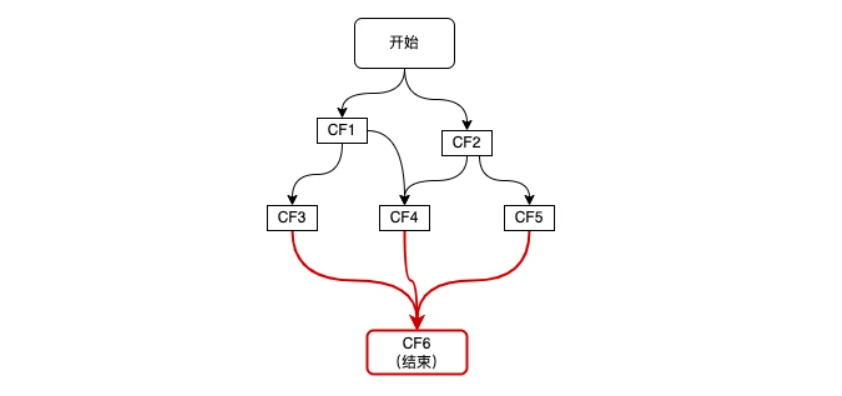
如上图红色链路所示,整个流程的结束依赖于三个步骤CF3、CF4、CF5,这种多元依赖可以通过allOf或anyOf方法来实现,区别是当需要多个依赖全部完成时使用allOf,当多个依赖中的任意一个完成即可时使用anyOf,如下代码所示:
CompletableFuture<Void> cf6 = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf3, cf4, cf5);CompletableFuture<String> result = cf6.thenApply(v -> { //这里的join并不会阻塞,因为传给thenApply的函数是在CF3、CF4、CF5全部完成时,才会执行 。 result3 = cf3.join(); result4 = cf4.join(); result5 = cf5.join(); //根据result3、result4、result5组装最终result; return "result";});注意点
1. Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { int a = 0; int b = 666; int c = b / a; return true; },executorService).thenAccept(System.out::println);
//如果不加 get()方法这一行,看不到异常信息 //future.get();Future需要获取返回值,才能获取到异常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。小伙伴们使用的时候,注意一下哈,考虑是否加try…catch…或者使用exceptionally方法。
参考文章
基础篇:异步编程不会?我教你啊!CompletableFuture(JDK1.8) - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
CompletableFuture原理与实践-外卖商家端API的异步化 - SegmentFault 思否
Java CompletableFuture 详解 (colobu.com)